Graduate Hiring Trends in India are witnessing a seismic shift as the nation adapts to onboarding its burgeoning graduate population. Traditional metrics and conventional approaches are no longer adequate to address the complexities of a rapidly evolving economy and a digitally native generation entering the workforce.
The confluence of technological advancements, changing employer expectations, and the aspirations of Gen Z are reshaping the very fabric of graduate hiring trends in India. In this article we will delve deep into the multifaceted challenges and emerging strategies that define the future of how Indian graduates find their place in the professional world, drawing insights from recent comprehensive reports that have captured the pulse of this dynamic ecosystem.
The Shifting Sands of Employer Expectations in Graduate Hiring Trends India.
For years, the pursuit of graduates often centred around the prestige of their alma mater. Premier college tags were perceived as a reliable proxy for talent and potential. However, the Unstop Talent Report 2025 throws a compelling curveball into this long-held assumption, revealing that a significant 73% of recruiters now assert that premier college tags do not significantly impact their hiring decisions. This marks a profound departure from tradition and signals a fundamental recalibration in graduate hiring trends in India. Why this shift? The report emphasizes a growing focus on talent over tags, indicating that employers are increasingly prioritizing demonstrable skills and real-world abilities over the perceived pedigree of an institution.
Furthermore, the India’s Graduate Skill Index 2025 corroborates this emphasis on capabilities, highlighting that while overall graduate employability saw a marginal dip, employability in technical roles has increased. This suggests that companies are actively seeking graduates equipped with specific technical proficiencies relevant to the demands of an AI-enabled workplace.
Could it be that the rapid pace of technological change has rendered traditional academic credentials less indicative of immediate job readiness? It certainly seems so.
Moreover, the Unstop report sheds light on the specific skills recruiters are actively seeking. Communication & interpersonal skills (72%), problem-solving & critical thinking (59%), and adaptability & flexibility (56%) top the list of priorities. These findings align remarkably well with the WEF Future of Jobs Report 2025, which identifies analytical thinking, resilience, flexibility and agility, leadership and social influence, and creative thinking as top core skills sought by employers globally. This convergence underscores a universal recognition of the importance of both technical acumen and crucial soft skills in navigating the future of work, a key facet of understanding graduate hiring trends in India.
The Gen Z Factor: Aspirations and Expectations Shaping Graduate Hiring Trends India
The generation entering the workforce today, Gen Z, brings with it a unique set of aspirations and expectations that are significantly influencing graduate hiring trends in India. They aren’t just looking for a job; they are seeking “a game worth playing”, as aptly put by the Unstop report. This signifies a desire for roles that offer meaning, growth, and opportunities for impact, rather than simply a paycheck.
The Unstop report highlights that Gen Z’s definition of growth extends beyond traditional hierarchical promotions. They value upward movement (vertical or lateral), empowerment to lead, social impact & sustainability, and tech-driven & transparent workplaces. This “QUEST mindset” dictates their career choices and influences the kind of companies they are drawn to. Are organizations adequately attuned to these nuanced expectations? The report suggests a potential gap, with traditional HR strategies perhaps not fully capturing what truly engages and retains this generation.
Furthermore, Gen Z places a high premium on engagement and interaction with potential employers. The Unstop report reveals that participating in company-led competitions (69%) and finding job or internship openings on job boards (67%) are the top two ways companies get on their radar. This indicates that active engagement and opportunities to prove their mettle are far more effective than passive employer branding activities. Why are only 25% of recruiters prioritizing competitions when nearly 70% of students across domains see them as crucial? This disconnect represents a missed opportunity for companies to connect with and assess top talent effectively, a critical consideration in shaping future graduate hiring trends in India.
The Persistent Skills Gap: A Major Challenge in Graduate Hiring Trends India
Despite the aspirations of graduates and the evolving priorities of employers, a significant challenge persists: the skills gap. The India’s Graduate Skill Index 2025 reveals that only 42.6% of Indian graduates who apply for jobs are employable. This sobering statistic underscores a fundamental mismatch between the skills possessed by graduates and the requirements of the industry, a critical hurdle in graduate hiring trends in India.
Interestingly, the report notes that the drop in employability is “particularly driven by non-technical skills,” while “employability in technical roles has seen an increase”. This suggests that while graduates are increasingly acquiring technical skills, perhaps through online courses and distance learning resources, the development of crucial soft skills like communication, critical thinking, and problem-solving is lagging. As the WEF report emphasizes the rising importance of both technical and socio-emotional skills, this gap in non-technical competencies presents a significant impediment to graduate employability in India.
Furthermore, the Unstop report highlights the skills recruiters are prioritizing, such as communication & interpersonal skills (72%) and problem-solving & critical thinking (59%). The fact that employability in these areas is contributing to the overall low employability rate indicates a pressing need for educational institutions and graduates themselves to focus more deliberately on cultivating these essential skills. In this AI-augmented world, while machines handle analytical tasks, the ability to collaborate effectively, communicate persuasively, and think critically remains unequivocally human and highly valued.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Graduate Hiring Trends in India
The pervasive influence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is undeniably reshaping graduate hiring trends in India. The India’s Graduate Skill Index 2025 points out that technical proficiency in AI and data analytics is no longer a niche requirement; it has become fundamental across various sectors. The report also notes a significant increase in the employability of graduates in AI & ML roles, indicating a growing demand for professionals equipped with these cutting-edge skills.
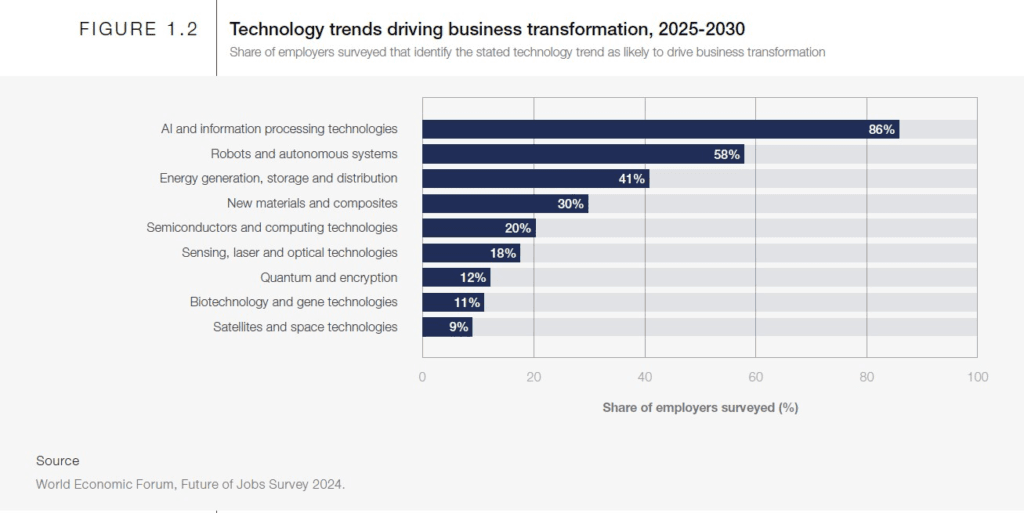
The WEF Future of Jobs Report 2025 echoes this sentiment, identifying AI and big data as the top fastest-growing skills globally. This technological wave is not just creating new roles like AI and Machine Learning Specialists; it’s also transforming existing ones, requiring graduates across various disciplines to possess a certain level of AI literacy and the ability to work alongside AI-powered tools.
However, the integration of AI also necessitates a renewed focus on human-centred skills. As machines take over repetitive and analytical tasks, skills like emotional intelligence, creativity, empathy, and ethical decision-making become even more critical differentiators. The WEF report emphasizes that even in an age of GenAI, skills requiring nuanced understanding, complex problem-solving, and sensory processing show limited risk of replacement, affirming the continued importance of human oversight. Therefore, graduate hiring trends in India are not just about finding tech-savvy individuals but also those who can blend technical skills with uniquely human capabilities.
Strategies for Navigating the Future of Graduate Hiring Trends in India
In light of these challenges and evolving dynamics, what strategies can be adopted by both employers and graduates to navigate the future of graduate hiring trends in India successfully?
For Employers:
- Prioritize Skills Over Pedigree: The data suggests a shift towards a skills-first approach. Employers should refine their hiring processes to focus on assessing demonstrable skills through behavioural interviews (65%), technical assessments (69%), peer interviews (35%), psychometric testing (35%), group assessments (29%), and trial projects/internships/simulations (23%). The Unstop report indicates these methods are considered most effective for candidate evaluation.
- Actively Engage with Gen Z: To attract top talent, companies need to move beyond traditional recruitment methods and actively engage with students on their preferred platforms. Participating in company-led competitions, posting on job boards, and leveraging employee advocacy on social media are crucial strategies highlighted by the Unstop report.
- Bridge the Engagement Gap: Recruiters need to recognize the disconnect between their preferred engagement methods and what works for students. Investing in and prioritizing competitions can be a powerful tool for both engagement and talent identification.
- Re-evaluate Employer Branding: Employer branding should focus on “real experiences that make students take notice”, rather than just generic job posts. Highlighting growth opportunities, company culture, and the potential for impact can resonate strongly with Gen Z.
- Invest in Upskilling and Reskilling: Recognizing the skills gap, companies must actively invest in training and development programs to upskill new hires and reskill existing employees. The WEF report highlights that 85% of employers plan to prioritize upskilling their workforce. Embedding models like the 80-10-10 learning framework can facilitate continuous on-the-job learning and skill development.
- Foster a Culture of Growth and Feedback: To retain Gen Z talent, companies need to cultivate a culture that supports growth beyond promotions and provides frequent and constructive feedback [Me]. Implementing reverse mentoring programs can also help leadership understand the perspectives and aspirations of younger employees.
- Embrace Flexibility and Well-being: Gen Z values transparency, inclusivity, and flexibility. Offering remote or hybrid work options and prioritizing employee mental health and well-being can significantly enhance a company’s attractiveness as an employer.
For Graduates:
- Focus on Skill Development: Graduates need to proactively focus on developing both technical and soft skills that are in high demand. This includes actively seeking internships, participating in practical projects, and utilizing online learning resources to acquire relevant competencies.
- Prioritize Practical Experience: The emphasis on experience over academic pedigree means that internships and practical projects hold significant weight. Graduates should seek out opportunities to gain real-world experience and build a strong portfolio of work.
- Cultivate Essential Soft Skills: While technical skills are crucial, graduates must also consciously develop their communication, critical thinking, problem-solving, and adaptability skills. Participating in group projects, presentations, and extracurricular activities can help hone these essential competencies.
- Engage with Companies Proactively: Instead of passively waiting for job offers, graduates should actively engage with companies they are interested in through competitions, networking events, and by leveraging online platforms.
- Understand the Evolving Job Landscape: Staying informed about emerging technologies and the skills in demand is crucial. Resources like the Unstop Talent Report and the India’s Graduate Skill Index can provide valuable insights into graduate hiring trends in India.
- Embrace Continuous Learning: In a rapidly evolving job market, a mindset of continuous learning is essential. Graduates should be prepared to adapt to new technologies and acquire new skills throughout their careers.
Here’s What I Think:
In my opinion, the evolving landscape of graduate hiring trends in India presents both significant challenges and exciting opportunities. The shift away from a sole focus on premier college tags towards a more skills-centric approach is a welcome development, as it has the potential to democratize opportunities and recognize talent from a wider range of institutions. I believe this recalibration is crucial for India to fully leverage the potential of its vast graduate population.
However, the persistent skills gap remains a major concern. It underscores the need for a more effective alignment between academic curricula and industry requirements. Educational institutions, in collaboration with industry leaders, must proactively adapt their programs to equip graduates with the skills that are truly valued in the modern workplace. Furthermore, graduates themselves must take ownership of their skill development, actively seeking out opportunities to bridge this gap.
The influence of Gen Z’s aspirations is also a powerful force shaping graduate hiring trends in India. Their desire for meaningful work, growth opportunities, and a positive work culture necessitates a fundamental shift in how companies attract and retain young talent. I believe that organizations that are genuinely attuned to these expectations and are willing to adapt their strategies will be the winners in the long run.
Finally, the integration of AI into the workplace presents a transformative dynamic. While it creates a demand for new technical skills, it also amplifies the importance of uniquely human capabilities. In my view, the future of graduate hiring trends in India lies in finding individuals who possess a balanced blend of both – those who are not only tech-savvy but also possess the crucial soft skills that enable effective collaboration, critical thinking, and ethical decision-making in an AI-augmented world. Navigating this evolving landscape will require a collaborative effort from educational institutions, employers, and graduates themselves, all working towards a future where talent is truly recognized and nurtured, regardless of tags or traditional benchmarks.
Sources of Insights:

Ajay Dhage is a seasoned talent acquisition leader with over 20 years of experience in Talent Acquisition and Workforce Strategy across the oil and gas, EPC, and renewables sectors. As Talent Acquisition Lead for a global Oil & Gas EPC company in India, he manages the end-to-end hiring lifecycle for complex, multi-disciplinary projects, from sourcing and assessment to onboarding and workforce planning. Known for his customer-focused approach and innovative use of AI and data in hiring, Ajay focuses on building future-ready workforces and resilient leadership pipelines. Through ajayable.com, he shares insights, trends, and practical frameworks to help HR professionals, organisations, and recruiters excel in a rapidly evolving, competitive talent landscape.