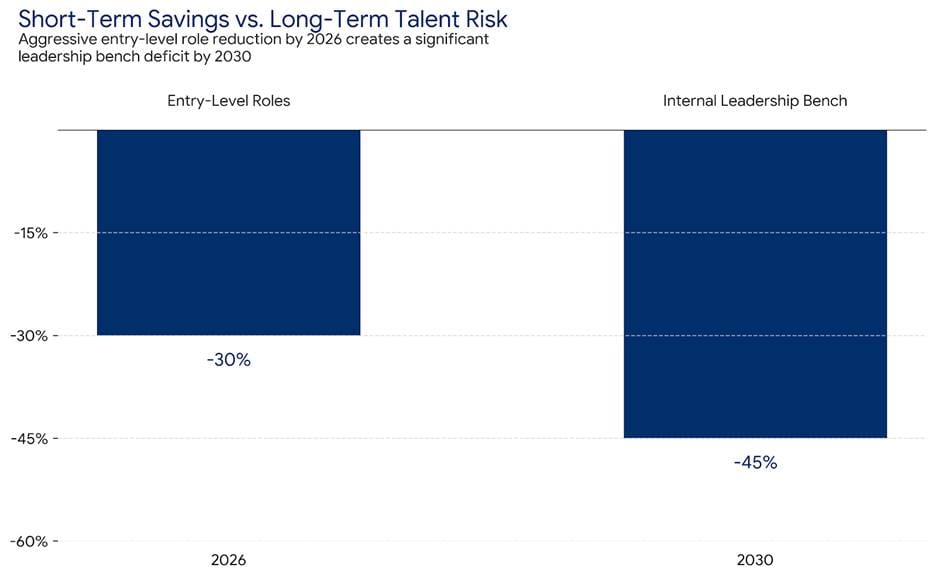
In 2026, boardrooms will applaud efficiency. Leaders will point to payroll reductions, automated workflows, and short-term margin gains. The Leadership Pipeline Crisis begins here. I believe many organisations mistake financial neatness for strategic strength. By stripping out entry-level roles in pursuit of cost control, companies hollow out the very system that produces future leaders. What looks disciplined today sets up operational fragility tomorrow.
The numbers seduce. Sixty four percent of executives plan AI-driven headcount reductions, with junior and back-office roles first on the list. These positions appear expendable. In my opinion, they represent the apprenticeship layer of leadership. Remove the base, and the pyramid collapses. If entry-level employees vanish in 2026, who will carry institutional memory in 2030?
Short-Term Savings Create Long-Term Leadership Risk
Efficiency wins budgets. Talent debt destroys futures.
Boards reward fast results. Replacing junior roles with automation trims millions from operating costs. Research shows forty three percent of firms plan to replace roles with AI, targeting operations and entry-level staff. The Leadership Pipeline Crisis hides behind these numbers.
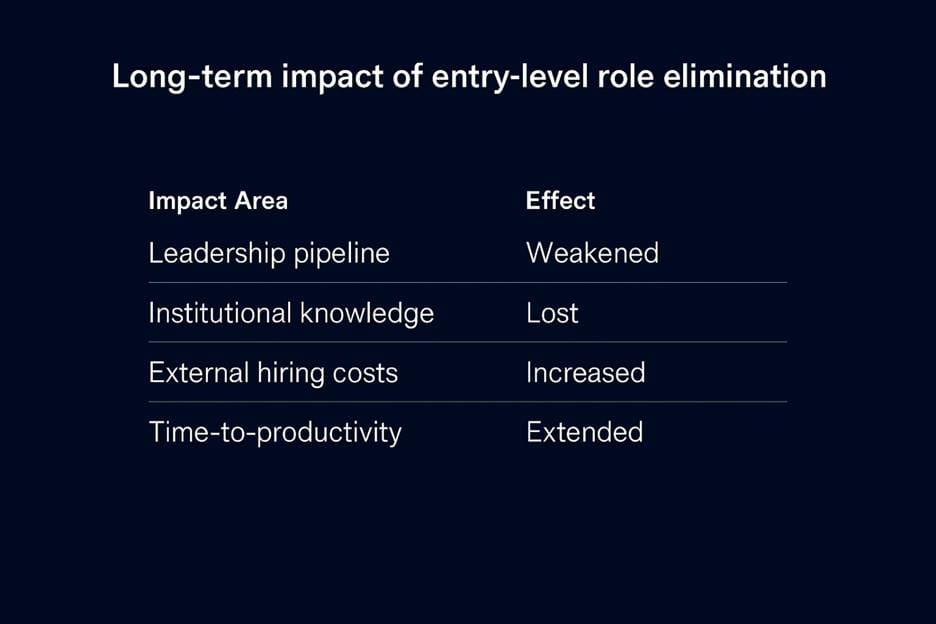
Every senior leader once started in those roles. Eliminate the entry point, and the journey ends before it begins. I believe modern efficiency misses a basic truth. The coordinator who understands every workaround becomes the manager who stabilises chaos. When the coordinator disappears, the feeder system fails. A balance sheet shows savings. The organisation absorbs structural damage.
Entry-Level Roles Anchor Institutional Knowledge
Leadership forms through exposure, not instruction.
Institutional knowledge lives outside manuals. It passes through observation, repetition, and context. Entry-level employees absorb how decisions get made, who influences outcomes, and where risks hide. This learning underpins the Leadership Pipeline Crisis.
David Ellis of Korn Ferry warns against halting junior hiring. Early-career professionals adopt technology faster than any other group. They translate tools into practice. When organisations cut these roles, competitors who retain them move faster. Agility follows people, not software.
Without internal pipelines, firms buy leadership externally. External hires cost more, integrate more slowly, and lack cultural context. Is a million saved today worth five million in search fees and failed transitions later? I believe most boards never run this math.
AI Agents Accelerate the Leadership Pipeline Crisis
Automation removes the work that teaches judgment.
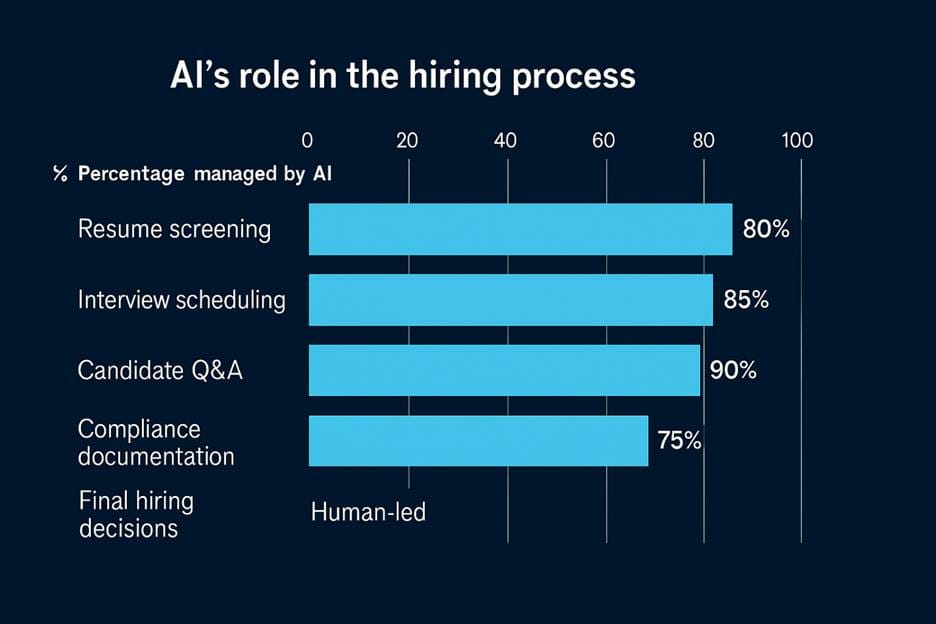
By 2026, AI agents stop assisting and start operating. Entire workflow segments run without human intervention. Up to eighty per cent of transactional recruitment and administrative activity shifts to machines. This marks an inflexion point in the Leadership Pipeline Crisis.
AI twins free fifteen hours per employee each week. Productivity rises. Learning opportunities shrink. In my experience, administrative work trains professional instinct. Scheduling interviews teaches stakeholder dynamics. Resume screening teaches pattern recognition. When machines absorb this work, junior employees lose the training ground where judgment forms.
The result is not fewer people. It is fewer people with seasoned judgment.
The Skills Gap Widens the Leadership Pipeline Crisis
Technical fluency grows faster than human capability.
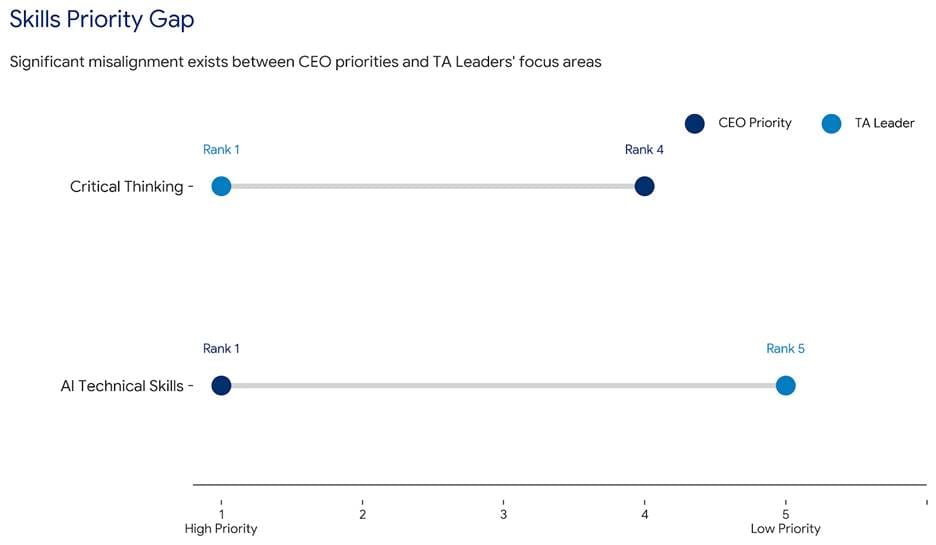
Sixty three percent of employers identify the skills gap as the main barrier to transformation through 2030. Here lies the paradox. AI-led job cuts widen the very gap leaders fear.
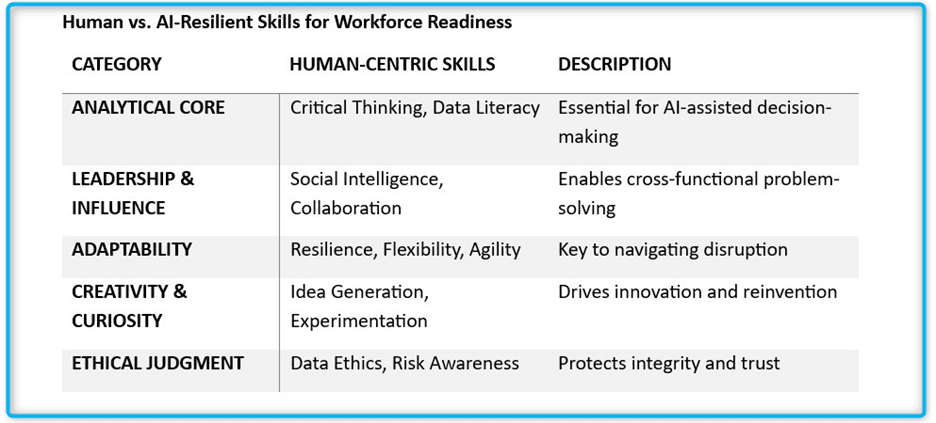
Executives chase AI expertise. Talent leaders prioritise critical thinking and problem-solving. Technical skills rank fifth. Why? Tools teach fast. Judgment develops slowly. Anyone learns prompting in weeks. Questioning output takes years.
A workforce fluent in tools but weak in evaluation fuels the Leadership Pipeline Crisis. When leaders lack the instinct to challenge machine output, risk multiplies.
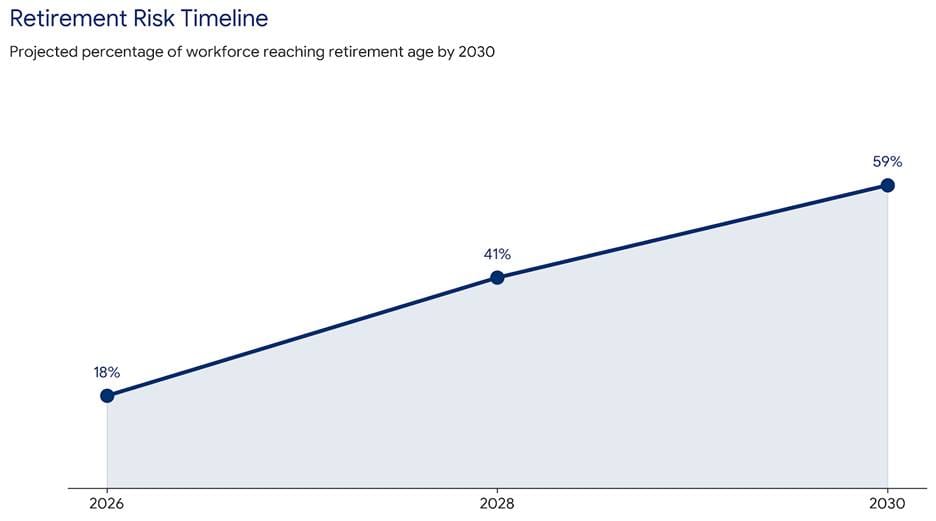
Boomer Retirements Drain Leadership Capacity
Experience exists as apprentices disappear.
Retirements accelerate in 2026. Fifty nine percent of workers over fifty-five plan to retire within five years. Seventy two percent of managers fear losing critical expertise. The Leadership Pipeline Crisis intensifies from both ends.
Experienced mentors exit. Entry-level mentees never arrive. Knowledge transfer collapses. I believe organisations miss a simple buffer. Short-term rehiring of retirees buys time. It enables mentoring, documentation, and succession. Cost obsession blocks patience. The bridge collapses from both sides.
Redesigning Roles to Protect the Leadership Pipeline
Human work must evolve, not vanish.
The answer lies in redesign, not resistance. Organisations must stop eliminating junior roles and start reshaping them. AI handles routine tasks. Humans practice judgment, advisory work, and relationship management.
Return on investment must include biological return. If automation saves fifteen hours weekly, leaders must reinvest those hours into complex decision-making. Talent acquisition shifts from a cost centre to a strategic capability.
In my opinion, firms that survive the Leadership Pipeline Crisis treat early-career hiring as precision development, not volume intake.
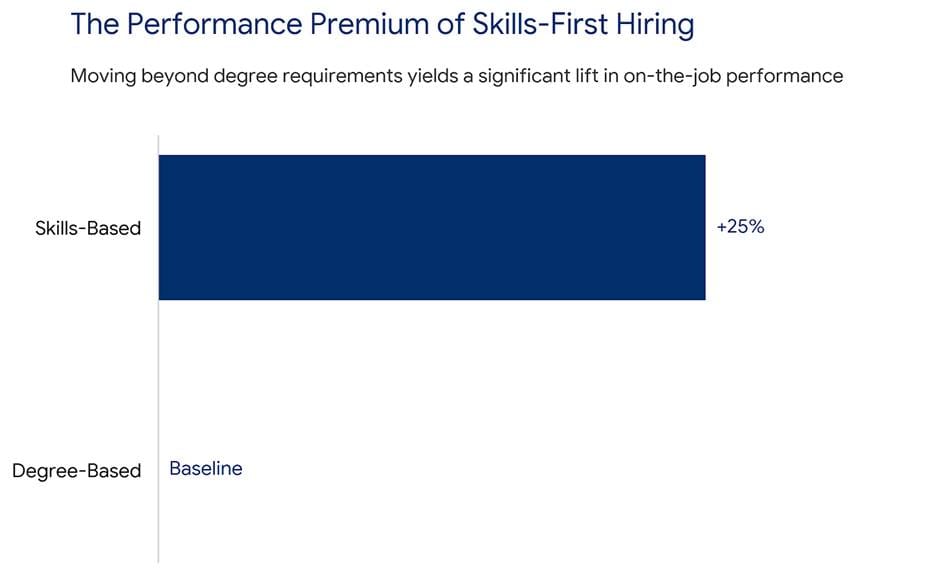
Skills-First Hiring Strengthens the Leadership Pipeline
Ability outperforms pedigree.
Degrees lose dominance. Only forty one percent of job seekers view degrees as essential. Skills-first hiring expands access and accuracy.
Ninety per cent of firms using skills-based hiring report fewer hiring mistakes. Ninety four percent see stronger performance. Skills verification now happens instantly through digital credentials. Ability replaces background.
I believe skills-first hiring stands as a structural defence against the Leadership Pipeline Crisis. Future leaders solve problems. Credentials are never guaranteed.
Internal Mobility Builds Leadership Capacity
The next leader already works inside.
External markets fluctuate. Internal capability compounds. Fifty one percent of employers plan to redeploy talent internally. The Leadership Pipeline Crisis often reflects imagination failure.
Internal talent marketplaces reveal transferable skills. AI supports matching and learning pathways. Careers shift from ladders to networks. When organisations invest in growth, employees invest in outcomes.
If leaders of 2030 cannot be hired, they must be built.
Data Storytelling Makes the Leadership Pipeline Visible
Boards respond to evidence, not warnings.
Recruitment success no longer rests on time-to-fill. It rests on impact. Talent leaders must prove performance, retention, and revenue contribution.
Quality of hire declines when automation dominates. Cost-per-hire improves. Boards see one metric and miss the risk. In my opinion, the Leadership Pipeline Crisis persists because boards track the wrong signals. Ultimately, predictive analytics and human judgment will decide who wins.
Leaders who connect hiring data to business outcomes secure sponsorship and budget.
Human and AI Teams Demand New Leadership
The challenge shifts from technology to trust.
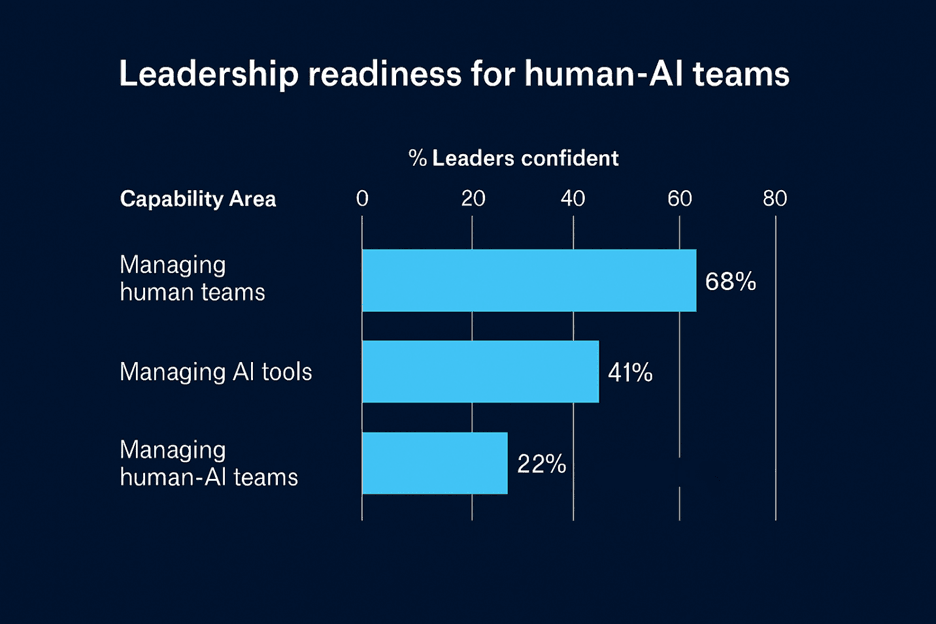
Hybrid teams define 2026. Yet only twenty two percent of leaders trust managers to lead humans and AI together. This gap feeds the Leadership Pipeline Crisis.
Managers must know when to override machines, manage conflict, and coordinate mixed teams. AI-ready leaders translate strategy into execution. Software equalises access Human judgment differentiates outcomes. Ultimately, it is the human edge—essential capabilities, not AI—that will define the future of work.
Here’s What I Think
The next five years belong to workforce orchestrators. Talent leaders’ step beyond operations into strategic authority. Those who reclaim time through AI become advisors on transformation.
But hollow organisations fail regardless of technology. Eliminating entry-level roles for margin equals corporate cannibalism. The future gets consumed to fund the present.
I believe the human machine frontier demands a new idea. Silicon mentorship. AI should capture retiring knowledge and train early-career talent. Apprenticeship programs should hire a junior human and an AI agent together.
Ground these actions now:
- Replace headcount reduction with talent elevation. Reinvest automation savings into reskilling.
- Test critical thinking in every interview. Machines handle proficiency.
- Redesign entry-level roles into specialised tracks from day one.
- Quantify the Leadership Pipeline Crisis. Show boards when leadership supply collapses.
The future of work is not speed. It is structured. Leadership in 2030 depends on which organisations develop today. Software scales. People decide.

Ajay Dhage is a seasoned talent acquisition leader with over 20 years of experience in Talent Acquisition and Workforce Strategy across the oil and gas, EPC, and renewables sectors. As Talent Acquisition Lead for a global Oil & Gas EPC company in India, he manages the end-to-end hiring lifecycle for complex, multi-disciplinary projects, from sourcing and assessment to onboarding and workforce planning. Known for his customer-focused approach and innovative use of AI and data in hiring, Ajay focuses on building future-ready workforces and resilient leadership pipelines. Through ajayable.com, he shares insights, trends, and practical frameworks to help HR professionals, organisations, and recruiters excel in a rapidly evolving, competitive talent landscape.