The foundations of the global labour market have shifted. Today, a growing number of college-educated young adults are abandoning the assumed straight line from degree to desk and choosing skilled trades instead. That choice is not a retreat. It is a strategic recalibration driven by economic pressure, automation anxiety, and the realisation that hands-on, high-skill work often resists replacement by software. I believe this movement marks the rise of a new class of professionals — Skilled Trades Innovators — and it demands a strategic response from leaders and organisations.
The Strategic Career Pivot
A structural, not cyclical, reordering of career expectations driven by risk, debt, and durable value.
For decades, the professional script was simple. A college degree promised upward mobility and white-collar stability. That script is fraying. Recent data show 37 per cent of Gen Z college graduates are now working in or actively pursuing blue-collar roles. That figure is not anecdotal. It is the signal of a large-scale reallocation of human capital toward roles perceived as resilient to automation and immediately in earning potential.
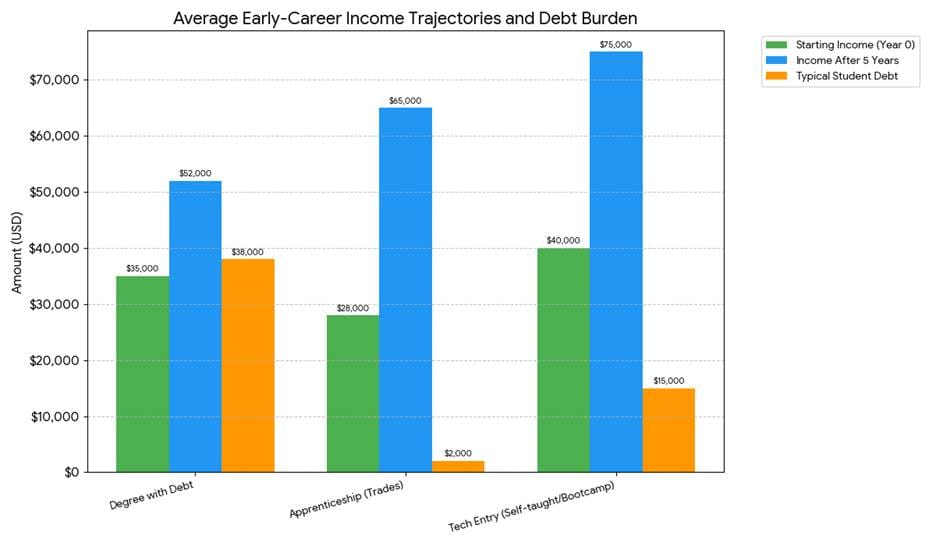
This pivot is rational. Graduates face heavy debt burdens, a sluggish entry-level job market, and a technology wave that can hollow out clerical and standardised knowledge work. The decision to pivot into trades is a hedged bet. It trades uncertain returns on a degree for paid apprenticeships, a faster path to income, and what many graduates see as work that will remain necessary regardless of algorithmic progress.
Skilled Trades Innovators and the AI Calculus
Young professionals are choosing roles where cognition meets craft because those roles are harder to automate.
Generative AI and automation have changed how entrants assess career risk. Roughly one quarter of graduates entering trades cite AI resilience as a key reason for their choice. Organisations across industries already anticipate major transformation. One study notes that 41 percent of organisations expect to reduce their workforce before 2030 as a result of automation. Employers predict that AI and information processing technologies will transform most operations within a few years. These expectations shape risk perception for a generation steeped in digital fluency.
Put simply, AI is exceptionally good at pattern recognition, optimisation, and repeatable cognitive tasks. It struggles in non-standard physical environments where human judgement, real-time improvisation, and manual problem-solving matter. Wiring a house, diagnosing a machine in an unpredictable setting, or adapting to on-site anomalies are tasks where human skill remains essential. Skilled Trades Innovators combine cognitive skills with situational dexterity. That mix makes them hard to replace.

Economics That Explain the Shift
Debt, earnings reality, and immediate paid training make trades a rational financial choice.
Financial calculus drives behaviour. The average student loan debt is over $38,000. For many graduates, the return on a degree is uncertain. Study reports that 19 percent of graduates shifted to blue-collar work because they could not find roles in their field, 16 percent because they were not earning enough, and another 16 percent because their degree did not lead to the expected career. Paid apprenticeships invert the traditional investment model. They offer on-the-job income from day one and reduce dependence on loans.
Wages in skilled trades are better than the stereotype implies. Experienced electricians, plumbers, and HVAC technicians report median wages in the $60,000 to $80,000 range. Top performers often surpass six figures. When you factor in job security, fewer debts, and clear progression to entrepreneurship or business ownership, the long-term financial narrative for trades is compelling.
Skilled Trades Innovators: High-Tech, High-Touch Work
Modern trades are cognitive workzones where analytical skill and hands-on capability converge.
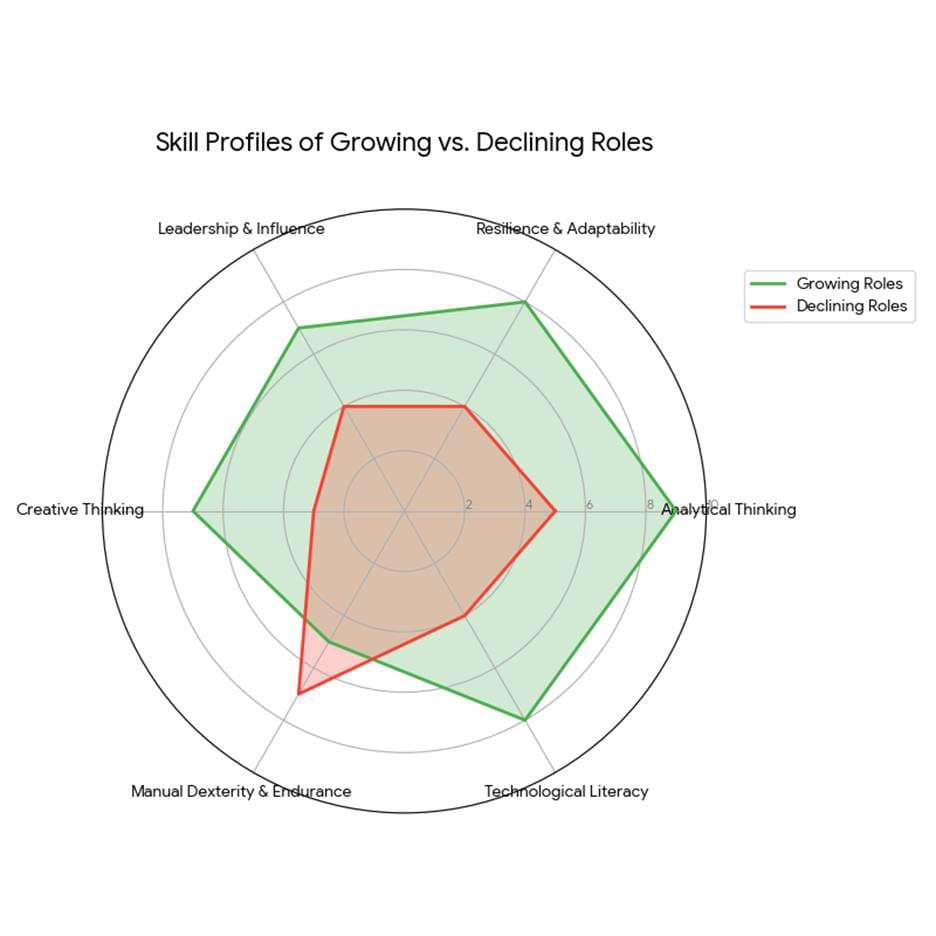
A persistent misperception is that blue-collar work equals low-tech labour. The reverse is true in many growth areas. Manufacturing uses advanced robotics and machine vision. Electricians integrate smart building systems. Solar and wind technicians work with power electronics and grid software. The tradecraft of 2025 demands analytical thinking, systems literacy, and the ability to manage automation. The World Economic Forum data lists analytical thinking, resilience, leadership, and creative thinking among the most valued skills. Those are the exact capabilities college education cultivates. A graduate who understands systems thinking and can apply it to physical infrastructure becomes a multiplier in any trade setting.
Skilled Trades Innovators and the Green Transition
Decarbonisation creates durable demand for trade skills tied to new infrastructure.
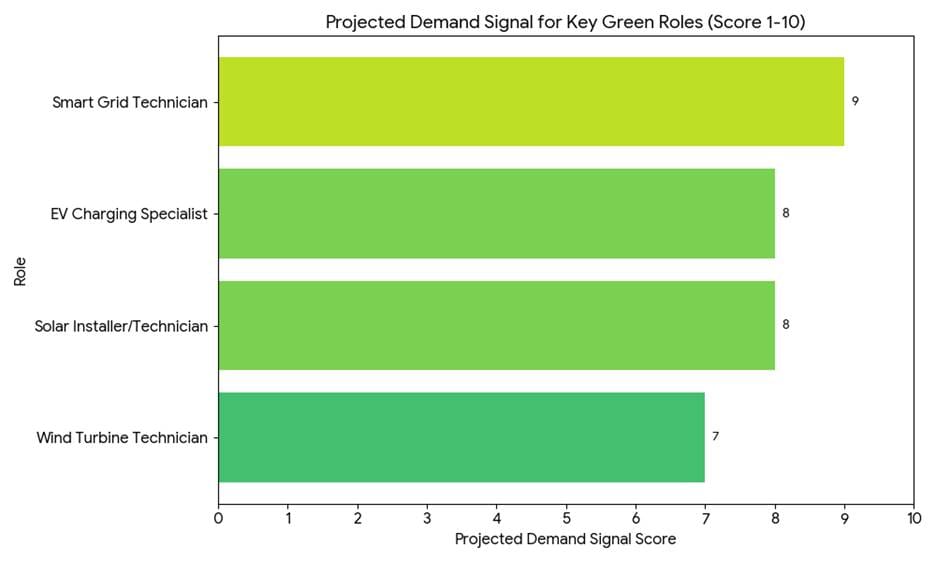
Energy transition and climate adaptation are structural demand drivers. Nearly half of surveyed employers anticipate emissions reduction efforts will be a major driver of organisational transformation. Investments in climate adaptation are close behind. Those priorities create demand for roles like renewable energy technicians, electric vehicle specialists, and environmental engineers. These roles require practical installation and maintenance skills plus the ability to engage with digital monitoring systems and smart grids. Skilled Trades Innovators who acquire green specialisations will find exceptional wage growth and mobility.
Skilled Trades Innovators in a Churning Global Market
Structural labour-market churn plus weak entry-level hiring make trades an attractive, available path.
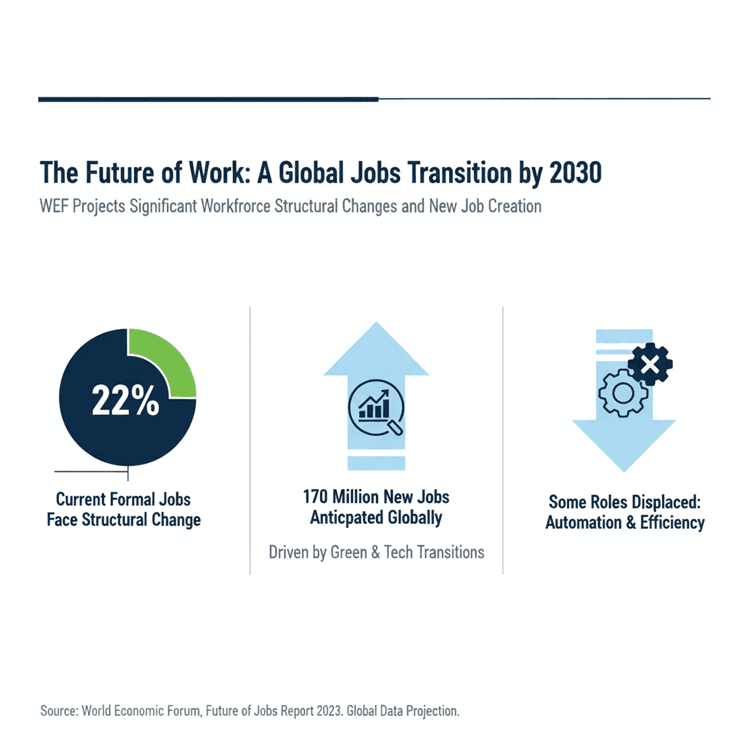
Global labour markets are in flux. Youth unemployment is markedly higher than aggregate unemployment in many regions. Youth unemployment rates such as 10.8 percent in the United States and substantially higher rates in several emerging economies. Employers report that structural changes will affect a significant share of jobs by 2030, and yet they also forecast the creation of millions of new roles during this transition. In this context, trades offer immediate opportunity and a more predictable route to stable income. For employers, this is a chance to tap a resilient talent pool that other firms overlook.
How Employers Can Win Skilled Trades Innovators
Companies that reframe trades as innovation careers will secure a competitive advantage in talent and operations.
Leaders must stop treating the trades as a labour reserve and start treating them as strategic talent channels. That requires three tactical shifts.
- Design College-Graduate Apprenticeships. Create structured programs that respect the analytical background of graduates and accelerate pathway timelines. Offer leadership modules, technical certifications, and rapid role rotations. Show career maps that lead to foreman, project manager, and business owner roles.
- Offer Financial Incentives that Address Debt. Tuition assistance for certification, sign-on bonuses, and transparent pay bands make the total compensation proposition clear and competitive versus a debt-laden degree path.
- Adopt Skills-First Hiring. Reduce reliance on degree checkboxes and emphasise demonstrated competencies. Research shows employers are adopting skill-based hiring and prioritising work experience and pre-employment tests over university degrees. Use skills assessments, simulation-based hiring, and apprenticeship interviews.
These moves are not charity. They are strategic investments in operational resilience. Employers who build talent funnels into critical infrastructure roles will reduce vacancy costs, shorten time-to-competence, and retain institutional knowledge.
The Skills-First Imperative for Skilled Trades Innovators
Upskilling, not credentials, will determine who succeeds in a hybrid human-machine labour market.
Employers already intend to reskill their workforce at scale. The studies records that 85 percent of employers plan to offer retraining and 77 percent plan to provide AI training. What matters most is the content of that training. The skills differentiating growing roles are analytical thinking, resilience, programming and technological literacy. These are not academic niceties. They are practical tools for diagnosing, integrating, and optimising semi-autonomous systems on site.
For leadership teams, the mandate is clear. Invest in modular learning. Blend vocational instruction with systems engineering basics. Create competency ladders that pair hands-on craft with data literacy. In my experience, cross-trained individuals who can read a digital fault log, interpret sensor data, and then fix a physical fault will become the linchpins of industrial operations.
Here’s What I Think
This is not a nostalgia-driven return to physical labour. It is a forward-looking strategy for resilient, skilled work.
The great career pivot toward skilled trades is a rational, market-driven response to modern uncertainty. I believe that calling these roles “blue-collar” will be obsolete by 2035. The future rewards those who combine analytical acumen with applied skill. The Skilled Trades Innovators are not rejecting technology. They are embracing it on their terms. They are work designers who use systems thinking to make physical systems more reliable, efficient, and sustainable.
If you lead people or plan workforce strategy, act now. Double down on skills-first hiring. Build graduate-friendly apprenticeship tracks. Fund lateral reskilling for mid-career employees in declining roles. Reimagine compensation to reflect the scarcity and strategic value of these skills. Organisations that move aggressively to win talent wars will convert a potential talent shortage into an enduring competitive advantage.
Actionable Checklist for Leaders
Concrete steps you can start this quarter to attract and retain Skilled Trades Innovators.
- Launch a pilot college-graduate apprenticeship with a clear 12- to 24-month competency map.
- Create a tuition and certification fund targeted to green and automation-resistant trades.
- Replace degree-only job postings with skills-first descriptions and simulation-based assessments.
- Identify 3 mid-career roles at risk from automation and design reskilling pathways into trade specialisations.
- Publish transparent pay bands for trade roles and benchmark against local market median wages.
Skilled Trades Innovators are both a solution and a signal. They tell us which work will matter in a world of smarter machines. Leaders who recognise this shift will redesign hiring, compensation, and training to capture durable value. Those who cling to outdated credential hierarchies will watch the best talent choose security and agency over uncertain prestige.
Sources of insights:
World Economic Forum. (2025). The Future of Jobs Report 2025.
4 in 10 Gen Z College Grads Are Turning To Blue-Collar Work for Job Security
4 Forces Fueling Gen Z’s Shift To Blue‑Collar Jobs
The rising pressures for Gen Z in the global job market

Ajay Dhage is a seasoned talent acquisition leader with over 20 years of experience in Talent Acquisition and Workforce Strategy across the oil and gas, EPC, and renewables sectors. As Talent Acquisition Lead for a global Oil & Gas EPC company in India, he manages the end-to-end hiring lifecycle for complex, multi-disciplinary projects, from sourcing and assessment to onboarding and workforce planning. Known for his customer-focused approach and innovative use of AI and data in hiring, Ajay focuses on building future-ready workforces and resilient leadership pipelines. Through ajayable.com, he shares insights, trends, and practical frameworks to help HR professionals, organisations, and recruiters excel in a rapidly evolving, competitive talent landscape.